Heart disease remains a leading cause of death worldwide, and for many patients with severe heart failure, transplantation offers the best chance for survival and a better quality of life. Unfortunately, the shortage of available donor hearts has long limited this life-saving option.
Cardiac xenotransplantation the transplantation of genetically modified animal hearts into humans is an exciting and rapidly advancing solution that has the potential to transform heart transplantation. This innovative approach could provide an abundant and reliable source of healthy hearts, offering new hope to thousands of patients waiting for a transplant.
What Is Cardiac Xenotransplantation?
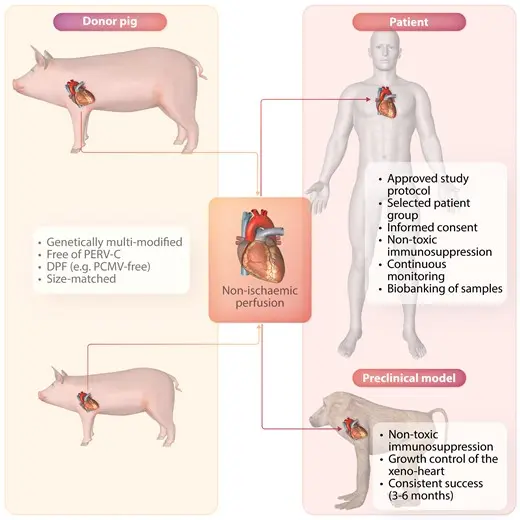
Cardiac xenotransplantation involves transplanting a heart from a specially modified pig into a human recipient. Thanks to advances in biotechnology, scientists can now create pig hearts that are more compatible with the human immune system, significantly reducing the risk of rejection.
Pigs are ideal donors because their hearts are similar in size and function to human hearts, and they can be bred quickly under controlled conditions, ensuring a steady and scalable supply of donor organs.
Advances Making Cardiac Xenotransplantation Possible
Genetic Engineering Breakthroughs
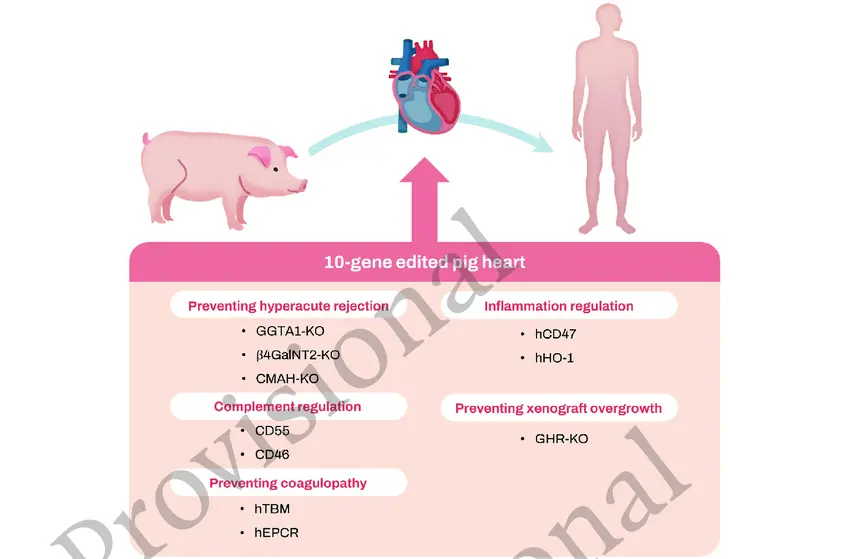
Innovative gene-editing tools such as CRISPR-Cas9 enable precise modifications to pig genomes. Scientists can remove genes responsible for immune rejection and add human genes to improve compatibility. These advances dramatically increase the chances that the transplanted heart will function well in the human body.
Immunological Progress
One of the greatest challenges in cardiac xenotransplantation is managing the recipient’s immune response to prevent rejection of the transplanted organ. Traditionally, organ transplant patients require lifelong immunosuppressive drugs, which can cause serious side effects including increased risk of infections and cancers.
Recent advances in immunology and biotechnology are paving the way for more precise and effective immune control strategies that aim to promote immune tolerance rather than just suppress immune activity. These novel approaches help the recipient’s immune system recognize the transplanted pig heart as “friendly,” significantly reducing the risk of rejection while minimizing the need for broad immunosuppression.
Key developments include:
- Targeted Immunomodulatory Therapies: Instead of weakening the entire immune system, therapies such as monoclonal antibodies selectively block specific immune pathways involved in rejection. For example, agents targeting the CD40-CD154 costimulatory pathway can prevent T-cell activation, a major driver of graft rejection.
- Cellular Therapies: Regulatory T cells (Tregs), which naturally suppress immune responses, can be expanded or engineered to promote long-term immune tolerance specifically toward the xenograft.
- Nanotechnology-based Approaches: Innovative delivery systems using nanoparticles can transport immunomodulatory molecules directly to the transplant site, enhancing efficacy while reducing systemic side effects.
Enhanced Safety Measures
Ensuring the safety of donor pig hearts is a top priority in cardiac xenotransplantation. One of the main concerns is the potential transmission of zoonotic infections—viruses or other pathogens that could pass from animals to humans during transplantation. To address this, cutting-edge screening technologies have been developed and integrated into the xenotransplantation process to detect and eliminate any infectious agents.
Exciting Clinical Successes
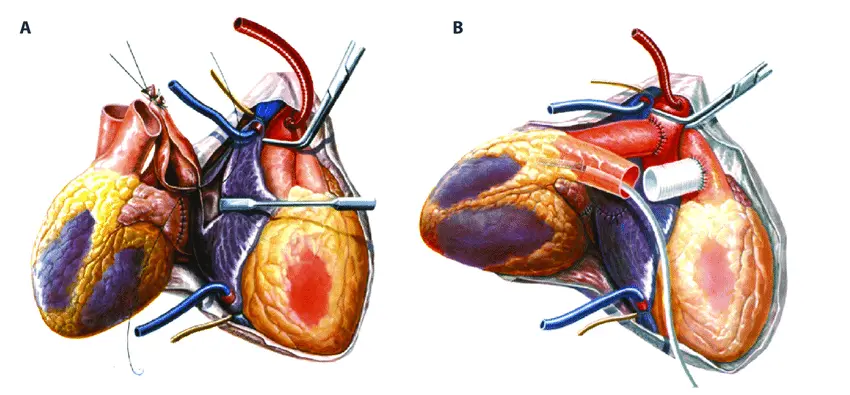
In recent years, cardiac xenotransplantation has moved from the laboratory to the clinic. Landmark surgeries, such as the first genetically modified pig heart transplant into a human patient, have demonstrated the feasibility of this approach and opened the door to wider clinical use.
Ongoing clinical trials worldwide continue to build on this momentum, aiming to improve long-term outcomes and make cardiac xenotransplantation a standard treatment option.
Why Cardiac Xenotransplantation Matters
- Expands the donor pool:
The shortage of human donor hearts is a critical barrier in treating patients with end-stage heart failure. Cardiac xenotransplantation offers a virtually unlimited supply of donor organs by using genetically modified pig hearts. This innovation has the potential to drastically reduce transplant waiting lists and prevent countless deaths caused by organ scarcity. Patients who might otherwise face years of waiting or no options at all could receive timely, life-saving transplants.
- Improves patient outcomes:
Genetic engineering enables the creation of pig hearts that are tailored to evade the human immune system’s rejection mechanisms. By removing problematic pig genes and adding human-compatible ones, these organs are better accepted by recipients’ bodies. This reduces complications such as acute rejection and chronic graft failure, leading to longer-lasting, healthier heart function and an improved quality of life for patients.
- Boosts healthcare innovation:
Cardiac xenotransplantation serves as a catalyst for advances across multiple fields of biomedical science. It drives progress in gene-editing technologies like CRISPR, enhances understanding of immune tolerance mechanisms, and accelerates breakthroughs in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. These technological leaps not only benefit xenotransplantation but also have wider applications for other diseases and therapies.
- Supports ethical practices:
The use of animal organs raises important ethical considerations. Controlled breeding programs for donor pigs ensure humane treatment and biosecurity standards. Biotechnology innovations reduce the need for animal testing by creating precise genetic modifications that minimize risks. Transparent regulatory frameworks and ongoing ethical oversight help balance the promise of saving human lives with respect for animal welfare, fostering responsible and sustainable development of this technology.
The Road Ahead: A Bright Future
The future of cardiac xenotransplantation is full of promise. With continued research and collaboration, we expect:
- More refined genetic modifications enhancing compatibility.
- Safer and more effective immune acceptance strategies.
- Better long-term success and quality of life for transplant recipients.
- Greater public awareness and acceptance of this transformative technology.
Cardiac xenotransplantation is a beacon of hope for patients suffering from heart failure. Powered by breakthrough biotechnology, it promises to overcome organ shortages and deliver new lives filled with health and vitality. As science advances and clinical experience grows, cardiac xenotransplantation is poised to revolutionize heart transplantation turning what was once science fiction into life-saving reality
For further information
Here you can find a current, comprehensive article on this topic:
Cardiac xenotransplantation: from concept to clinic